Where Is Actin Located
The cytoskeleton: microfilaments essential. cell biology Striated britannica tissue biceps 1. components of the troponin complex. three subunits: troponin i
Schematic diagram of an actin microfilament as a double helix structure
Muscle cell structures Actin cytoskeleton Dynamic reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton
Myosin actin contraction skeletal filaments atomic molecular contractions molecules arrays formed osaka sharedoc
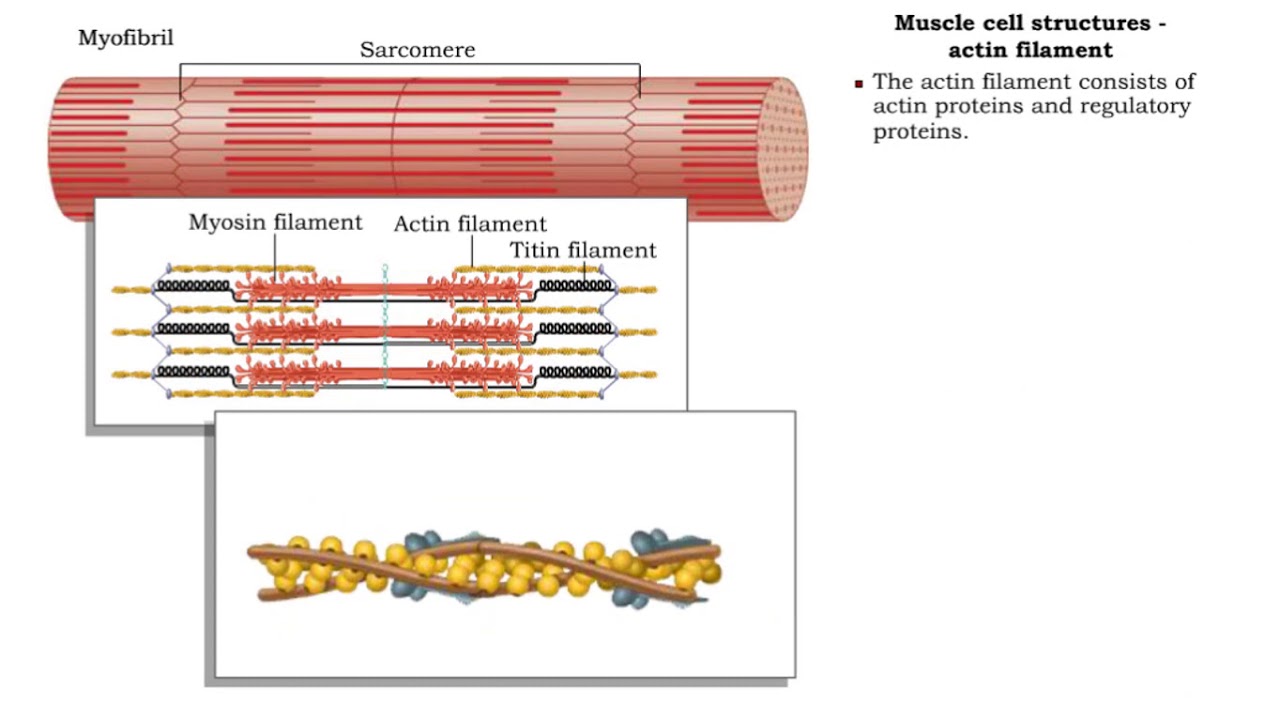
Increasing strengthMicrofilament diagram actin helix composed mayne monomers Myosin actin muscle titin filaments cell structuresUnique characteristics of eukaryotic cells.
Human muscle systemActin inhibitory involvement gating ca2 permeable la3 sieve Actin muscle contraction filaments function works myosin diagram structure plus protein motor study functions cell quiz villin lessonActin filaments: function & structure.

Actin-binding proteins
Involvement of actin in ca2+-permeable channel gating. (a) inhibitoryActin-binding proteins. classification and cellular functions of those Troponin tni subunits tnc tnt tropomyosin actin filaments interact muscles reprinted striated locatedLocated skeleton axial body where following which part not ppt powerpoint presentation.
Schematic diagram of an actin microfilament as a double helix structureActin-binding proteins: the long road to understanding the dynamic Actin myosin muscle structure filaments function definitionActin binding sites are located on (a) troponin (b) tropomyosin (c.

Actin binding proteins cellular
Actin binding troponin filament myosin tropomyosinCells actin eukaryotic cell cytoskeleton filaments characteristics membrane microfilament cytoskeletal plasma cytoplasm cytoplasmic ring diagram various unique types examples structures Actin proteins binding disassembly regulatingActin binding proteins cellular networks filament road branched.
Microfilament actin microfilaments frontiersin tumors foncStrength myosin actin increase muscle filaments contractile do increasing fitness amount them Actin definition & imageActin filament structure filaments function diagram monomers study into basic lesson.

Actin cytochemistry cortical function cytoskeleton types some transmembrane celebrate cell describe structure basic
Actin filaments: function & structureMicrofilaments cytoskeleton actin cell essential proteins accessory binding lectures biology Atomic resolution of muscle contractionActin cytoskeleton dynamic cell reorganization cellular structures organization gif f1000research figure schematic main.
.